Stability 1 year
Storage -80°C
Shipping Dry ice in continental US; may vary elsewhere
Background Reading
Desvergne, B., and Wahli, W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: Nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev 20 649-688 (1999).
Duplus, E., Glorian, M., and Forest, C. Fatty acid regulation of gene transcription. J Biol Chem 275(40) 30749-30752 (2000).
Gervois, P., Torra, I.P., Fruchart, J., et al. Regulation of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism by PPAR activators. Clin Chem Lab Med 38(1) 3-11 (2000).
Brown, P.J., Smith-Oliver, T.A., Charifson, P.S., et al. Identification of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ligands from a biased chemical library. Chem Biol 4 909-918 (1997).
Olefsky, J.M. Nuclear receptor minireview series. J Biol Chem 276(40) 36863-36864 (2001).
Clark, R.B. The role of PPARs in inflammation and immunity. J Leukoc Biol 71 388-400 (2002).
Show all 6 Hide all but first 3
Transcription Factor Binding Assay Buffer (4X) 1 ea
Transcription Factor Antibody Binding Buffer (10X) 1 ea
Transcription Factor Goat Anti-Rabbit HRP Conjugate 1 ea
Transcription Factor PPAR Competitor dsDNA 1 ea
Transcription Factor PPAR 96-Well Strip Plate 1 ea
Transcription Factor Developing Solution 1 ea
Transcription Factor Stop Solution 1 ea
Transcription Factor Reagent A 1 ea
Transcription Factor Complete PPARα Positive Control 1 ea
Transcription Factor Complete PPARδ Positive Control 1 ea
Transcription Factor Complete PPARγ Positive Control 1 ea
Transcription Factor Complete PPARα Primary Antibody 1 ea
Transcription Factor Complete PPARδ Primary Antibody 1 ea
Transcription Factor Complete PPARγ Primary Antibody 1 ea
Polysorbate 20 1 ea
Wash Buffer Concentrate (400X) 5 mL
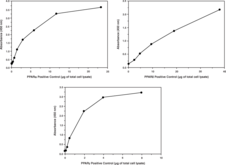
Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors (PPARs) are ligand-activated transcription factors belonging to the large superfamily of nuclear receptors.1,2 They are activated by a variety of fatty acids and fatty acid derivatives such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes. PPARs play pivotal roles in the regulation of lipid metabolism and homeostasis and are important indirect as well as direct regulators of cellular insulin sensitivity.3 There are three major PPAR isotypes; PPARα, PPARγ, and PPARδ/β which all bind to PPAR responsive elements (PPRE’s) as heterodimers with RXR, another member of the nuclear receptor superfamily. PPARα primarily activates genes encoding proteins involved in fatty acid oxidation, while PPARγ primarily activates genes directly involved in lipogenic pathway and insulin signaling.1,4,5 Members of the PPAR family are important direct targets of many antidiabetic and hypolipidemic drugs.6 Cayman’s PPARα, δ, γ Complete Transcription Factor Assay is a non-radioactive, sensitive method for detecting specific transcription factor DNA binding activity in nuclear extracts and whole cell lysates. A 96 well enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) replaces the cumbersome radioactive electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). A specific double stranded DNA (dsDNA) sequence containing the PPAR response element is immobilized onto the bottom of wells of a 96 well plate. PPARs contained in a nuclear extract, bind specifically to the PPAR response element. PPARα, δ, or γ are detected by addition of specific primary antibodies directed against the individual PPARs. A secondary antibody conjugated to HRP is added to provide a sensitive colorimetric readout at 450 nm. Cayman’s PPARα, δ, γ Complete Transcription Factor Assay comes with a single plate that measures all three isoforms of PPARα, δ, and γ. There are enough reagents for one-third of a plate for each isoform.
1 Desvergne, B., and Wahli, W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: Nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev 20 649-688 (1999).
2 Clark, R.B. The role of PPARs in inflammation and immunity. J Leukoc Biol 71 388-400 (2002).
3 Olefsky, J.M. Nuclear receptor minireview series. J Biol Chem 276(40) 36863-36864 (2001).
4 Duplus, E., Glorian, M., and Forest, C. Fatty acid regulation of gene transcription. J Biol Chem 275(40) 30749-30752 (2000).
5 Gervois, P., Torra, I.P., Fruchart, J., et al. Regulation of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism by PPAR activators. Clin Chem Lab Med 38(1) 3-11 (2000).
6 Brown, P.J., Smith-Oliver, T.A., Charifson, P.S., et al. Identification of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ligands from a biased chemical library. Chem Biol 4 909-918 (1997).