服务热线
021-60498804
产品中心
/ Products Classification 点击展开+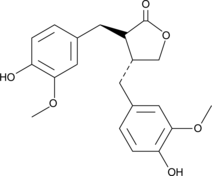
| Cat. Number | 080436490522144 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Name | Matairesinol |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
Background ReadingMorton, L.W., Caccetta, R.A., Puddey, I.B., et al. Chemistry and biological effects of dietary phenolic compounds: Relevance to cardiovascular disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 27 152-159 (2000). Ingram, D., Sanders, K., Kolybaba, M., et al. Case- Vanharanta, M., Voutilainen, S., Nurmi, T., et al. Association between low serum enterolactone and increased plasma F2-
Description
Diets high in fiber contain plant lignan species that may be directly responsible for some observed health benefits of these diets.1 Matairesinol is one of the principle lignans present in dietary fiber. It is absorbed directly, in addition to being further metabolized by enteric bacteria to enterolactone and enterodiol. Recent observations have shown an inverse association between serum enterolactone levels and serum isoprostane levels.2 This association implies a protective effect against oxidative injury associated with the dietary lignans themselves, enterolactone, or some intermediate in this pathway. There are also published reports of an inverse relationship between dietary lignans such as matairesinol and breast cancer incidence.3
1 Morton, L.W., Caccetta, R.A., Puddey, I.B., et al. Chemistry and biological effects of dietary phenolic compounds: Relevance to cardiovascular disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 27 152-159 (2000).
2
Vanharanta, M., Voutilainen, S., Nurmi, T., et al. Association between low serum enterolactone and increased plasma F2-
3
Ingram, D., Sanders, K., Kolybaba, M., et al. Case- |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
下一个:Isoliquiritigenin上一个:MCI-186 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||





