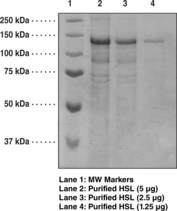
Peptide sequence:
2-1076 - Full length
·
Source:
Recombinant N-terminal His-tagged protein, expressed in Sf21 insect cells using a baculovirus expression system
·
Mr:
118.3 kDa
·
Hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) is a key enzyme regulating the mobilization of fatty acids from intracellular stores.1 There are three different isoforms of the enzyme: HSLadi, which is the predominant form found in adipocytes, HSLtes expressed in testes, and HSLb found in insulin secreting b-cells.2 The three isoforms are distinguished by their molecular masses.2 HSL catalyses the rate limiting step in the lipolysis of triacylglycerol, found in intracellular stores, to fatty acids (FA).3 HSL also catalyzes the hydrolysis of mono- and diacylglycerides, as well as cholesterol esters.4
1
Holm, C., Belfrage, P., Østerlund, T., et al. Hormone-sensitive lipase: Structure, function, evolution and overproduction in insect cells using the baculovirus expression system. Protein Eng 7(4) 537-541 (1994).
2
Krintel, C., Klint, C., Lindvall, H., et al. Quarternary structure and enzymological properties of the different hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) isoforms. PLoS One 5(6) (2010).
3
Zimmermann, R., Lass, A., Haemmerle, G., et al. Fate of fat: The role of adipose triglyceride lipase in lipolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791 494-500 (2009).
4
Saltiel, A.R. Another hormone-sensitive triglyceride lipase in fat cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(2) 535-537 (2000 Jan 18).