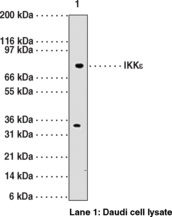
Antigen:
synthetic peptide corresponding to human IKKε amino acids 175-188, 526-540, and 567-580
·
Host:
rabbit
·
Application(s):
WB
·
Peptide sequence:
amino acids 175-188, 526-540, and 567-580
·
Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) is sequestered in the cytoplasm by the IκB family of inhibitory proteins that mask the nuclear localization signal of NF-κB, thereby preventing translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus.1 External stimuli such as tumor necrosis factor or other cytokines result in phosphorylation and degradation of IκB, releasing NF-κB dimers. NF-κB dimers subsequently translocate to the nucleus and activate target genes.2 IκB proteins are phosphorylated by IκB kinase complex consisting of at least three proteins, IKK1/α, IKK2/β, and IKK3/γ.3,4,5 Using a subtractive hybridization technique, a novel kinase, IKKε has been isolated.6 LPS increases IKKε mRNA levels in murine macrophage cell lines. This protein has significant sequence homology with kinase domains of IKK1/α and IKK2/β. Overexpression of wild-type IKKε in cells phosphorylates Ser32 and Ser36 of IκBα.
1
DiDonato, J.A., Hayakawa, M., Rothwarf, D.M., et al. A cytokine-responsive IκB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-κB. Nature 388 548-554 (1997).
2
Régnier, C.H., Song, H.Y., Gao, X., et al. Identification and characterization of an IκB kinase. Cell 90 373-383 (1997).
3
Verma, I.M., Stevenson, J.K., Schwarz, E.M., et al. Rel/NF-κB/IκB family: Intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev 9 2723-2735 (1995).
4
Verma, I.M., and Stevenson, J. IκB kinase: Beginning, not the end. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94 11758-11760 (1997).
5
Lin, A., Minden, A., Martinetto, H., et al. Identification of a dual specificity kinase that activates the Jun kinases and p38-Mpk2. Science 268 286-290 (1995).
6
Shimada, T., Kawai, T., Takeda, K., et al. IKK-i, a novel lipopolysaccharide-inducible kinase that is related to IκB kinases. Int Immunol 11(8) 1357-1362 (1999).