| References |
| Synonyms |
- Plasma Retinol Binding Protein 4
- pRBP
- sRBP4
|
| Formulation |
Peptide affinity-purified IgG |
| Stability |
1 year |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Wet ice
in continental US; may vary elsewhere
|
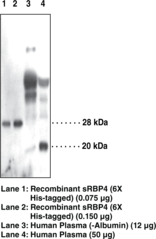
| Specificity |
|
Background Reading
Noy, N. Retinoid-binding proteins: Mediators of retinoid action. Biochem J 348 481-495 (2000).
Cowan, S.W., Newcomer, M.E., and Jones, T.A. Crystallographic refinement of human serum retinol binding protein at 2Å resolution. Proteins 8 44-61 (1990).
Yang, Q., Graham, T.E., Mody, N., et al. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 436 356-362 (2005).
Graham, T.E., Yang, Q., Blüher, M., et al. Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean, obese, and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med 354(24) 2552-2563 (2006).
Tamori, Y., Sakaue, H., and Kasuga, M. RBP4, an unexpected adipokine. Nat Med 12(1) 30-31 (2006).
Polonsky, K.S. Retinol-binding protein 4, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 354(24) 2596-2598 (2006).
Muoio, D.M., and Newgard, C.B. A is for adipokine. Nature 436 337-338 (2005).
Sivaprasadarao, A., and Findlay, J.B.C. Expression of functional human retinol-binding protein in Escherichia coli using a secretion vector. Biochem J 296 209-215 (1993).
Xie, Y., Lashuel, H.A., Miroy, G.J., et al. Recombinant human retinol-binding protein refolding, native disulfide formation, and characterization. Protein Expr Purif 14 31-37 (1998).
Show all 9
Hide all but first 3
| Size |
Global Purchasing |
| 500 µl |
|
Description
Antigen:
human sRBP4 amino acids 28-37 (RVKENFDKAR)
·
Host:
rabbit
·
Application(s):
WB
·
Serum retinol binding protein 4 (sRBP4) binds one equivalent of vitamin A and is one of the major retinol carriers found in the blood of mammals.1,2 Human RBP4 is a monomeric 21 kDa β-sheet-rich protein that contains three disulfide bonds and belongs to the lipocalin protein family.3 sRBP4 is synthesized and sequestered in hepatocytes until retinol binding triggers its secretion.3 In plasma, sRBP4 typically forms a 1:1 complex with the 55 kDa tetrameric protein transthyretin (TTR) which prevents RBP from being removed from the plasma by glomerular filtration.4 Recent studies have shown that sRBP4 is an adipocyte-derived “signal” that may contribute to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.5,6 Elevation of sRBP4 causes systemic insulin resistance whereas reduction of serum concentrations improves insulin action.5,7,8 The highest known concentrations of this protein exist in serum, liver, and skeletal muscle.9,10,11
1
Noy, N. Retinoid-binding proteins: Mediators of retinoid action. Biochem J 348 481-495 (2000).
2
missing reference text
3
Cowan, S.W., Newcomer, M.E., and Jones, T.A. Crystallographic refinement of human serum retinol binding protein at 2Å resolution. Proteins 8 44-61 (1990).
4
Sivaprasadarao, A., and Findlay, J.B.C. Expression of functional human retinol-binding protein in Escherichia coli using a secretion vector. Biochem J 296 209-215 (1993).
5
Yang, Q., Graham, T.E., Mody, N., et al. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 436 356-362 (2005).
6
missing reference text
7
missing reference text
8
missing reference text
9
Polonsky, K.S. Retinol-binding protein 4, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 354(24) 2596-2598 (2006).
10
Tamori, Y., Sakaue, H., and Kasuga, M. RBP4, an unexpected adipokine. Nat Med 12(1) 30-31 (2006).
11
missing reference text
|