| References |
| Synonyms |
|
| Stability |
1 year |
| Storage |
-80°C |
| Shipping |
Dry ice
in continental US; may vary elsewhere
|
Background Reading
Jones, P.D., Wolf, N.M., Morisseau, C., et al. Fluorescent substrates for soluble epoxide hydrolase and application to inhibition studies. Anal Biochem 343 66-75 (2005).
Imig, J.D., Zhao, X., Zaharis, C.Z., et al. An orally active epoxide hydrolase inhibitor lowers blood pressure and provides renal protection in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension 46(2) 975-981 (2005).
Yu, Z., Xu, F., Huse, L.M., et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase regulates hydrolysis of vasoactive epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Circ Res 87 992-998 (2000).
Chiamvimonvat, N., Ho, C., Tsai, H., et al. The soluble epoxide hydrolase as a pharmaceutical target for hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 50(3) 225-237 (2007).
Show all 4
Hide all but first 3
| Size |
Global Purchasing |
| 480 wells |
|
Description
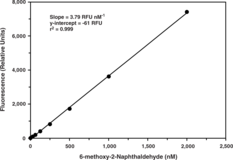
Mammalian soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is a member of the α/β-hydrolase fold family of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of exogenous and endogenous epoxides to vicinal diols. sEH is a homodimer consisting of two domains.1 The C-terminal domain is responsible for the epoxide hydrolase activity while the N-terminal domain has a catalytic center with phosphatase activity. Endogenous substrates for sEH include epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) which exhibit vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory activity.2 Inhibition of sEH in animal models was shown to effectively treat hypertension and vascular inflammation as well as related syndromes.3 These studies demonstrate the value for targeting sEH for development of small molecule inhibitors as therapeutics. Cayman’s sEH Cell-Based Assay Kit provides a convenient 96-well plate, fluorescence-based method for detecting epoxide hydrolase activity in whole cells. The assay utilizes Epoxy Fluor 7, a sensitive fluorescent substrate for sEH that can be used to monitor the activity of both human and murine enzymes.4 Hydrolysis of the substrate epoxide yields a highly fluorescent product, 6-methoxy-2-Naphthaldehyde, that can be monitored at excitation and emission wavelengths of 330 and 465 nm, respectively. 6-Methoxy-2-Naphthaldehyde is included to quantify enzyme activity and a recombinant sEH is included as a positive control. An sEH inhibitor AUDA is also included for checking specificity of the reaction. This assay parallels Cayman’s Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit (Catalog No. 10011671) which uses recombinant protein rather than whole cells for the assay. Together, both assays will help to identify whether or not an inhibitor/activator has a direct or indirect effect on the enzyme.
1
Chiamvimonvat, N., Ho, C., Tsai, H., et al. The soluble epoxide hydrolase as a pharmaceutical target for hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 50(3) 225-237 (2007).
2
Yu, Z., Xu, F., Huse, L.M., et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase regulates hydrolysis of vasoactive epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Circ Res 87 992-998 (2000).
3
Imig, J.D., Zhao, X., Zaharis, C.Z., et al. An orally active epoxide hydrolase inhibitor lowers blood pressure and provides renal protection in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension 46(2) 975-981 (2005).
4
Jones, P.D., Wolf, N.M., Morisseau, C., et al. Fluorescent substrates for soluble epoxide hydrolase and application to inhibition studies. Anal Biochem 343 66-75 (2005).
|