| References |
| Formal Name |
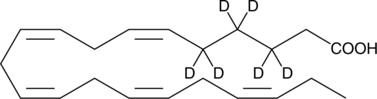
6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z,18Z-heneicosapentaenoic-3,3,4,4,5,5-d6 acid |
| Molecular Formula |
C21H26D6O2 |
| Formula Weight |
322.5 |
| Formulation |
A solution in ethanol |
| Purity |
>99% deuterated product |
| Stability |
1 year |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Wet ice
in continental US; may vary elsewhere
|
| SMILES |
CC/C=CC/C=CC/C=CC/C=CC/C=CCC([2H])([2H])C([2H])([2H])C([2H])([2H])C(O)=O
|
| Size |
Global Purchasing |
| 25 µg |
|
| 50 µg |
|
| 100 µg |
|
| 500 µg |
|
Description
Heneicosapentaenoic acid-d6 (HPA-d6) contains six deuterium atoms at the 3, 3’, 4, 4’, 5, and 5’ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of HPA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. HPA is a ω-3 fatty acid present in trace amounts in the green alga B. pennata Lamouroux and in fish oils. Its chemical composition is similar to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) except elongated with one carbon on the carboxyl end, placing the first double bond in the Δ6 position.1 HPA can be used to study the significance of the position of the double bonds in n-3 fatty acids. It incorporates into phospholipids and into triacylglycerol in vivo with the same efficiency as EPA and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and exhibits strong inhibition of arachidonic acid synthesis from linoleic acid.1 HPA is a poor substrate for PGH synthase and for 5-LO but retains the ability to rapidly inactivate PGH synthase.1
1
Larsen, L.N., Hovik, K., Bremer, J., et al. Heneicosapentaenoate (21:5n-3): Its incorporation into lipids and its effects on arachidonic acid and eicosanoid synthesis. Lipids 32 707-714 (1997).
|