| References |
| Formal Name |
5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenoic-5,6,8,9,11,12,14,15-d8 acid |
| CAS Number |
69254-37-1 |
| Molecular Formula |
C20H24D8O2 |
| Formula Weight |
312.5 |
| Formulation |
A solution in methyl acetate |
| Purity |
≥99% deuterated product |
| Stability |
1 year |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
Wet ice
in continental US; may vary elsewhere
|
| SMILES |
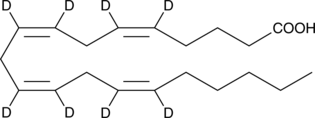
CCCCC/C=CC/C=CC/C=CC/C=CCCCC(=O)O
|
Background Reading
Nixon, A.B., Greene, D.G., and Wykle, R.L. Comparison of acceptor and donor substrates in the CoA-independent transacylase reaction in human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta 1300 187-196 (1996).
Burgoyne, R.D., and Morgan, A. The control of free arachidonic acid levels. Trends Biochem Sci 15 365-366 (1990).
| Size |
Global Purchasing |
| 1 mg |
|
| 5 mg |
|
| 10 mg |
|
| 50 mg |
|
Description
Arachidonic acid-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.1 Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-update of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.2
1
Burgoyne, R.D., and Morgan, A. The control of free arachidonic acid levels. Trends Biochem Sci 15 365-366 (1990).
2
Nixon, A.B., Greene, D.G., and Wykle, R.L. Comparison of acceptor and donor substrates in the CoA-independent transacylase reaction in human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta 1300 187-196 (1996).
|